Ophthalmology is a medical specialty that deals with the diagnosis, treatment and prevention of eye diseases. Modern technology in ophthalmology includes the use of lasers for various procedures. Diode lasers, known for their effectiveness and versatility, play an important role in ophthalmology. In this article, we will look at the use of diode lasers in ophthalmology, their benefits, and their various applications.
Application of diode lasers in ophthalmology:
Treatment of Retinopathy: Diode lasers are widely used to treat retinopathy, a condition characterized by damage to the retina. They are used to coagulate or sclerotherapy the affected areas of the retina, thus preventing the further development of the disease and preserving the patient’s vision.
Glaucoma treatment: Diode lasers can be used to perform laser trabeculoplasty, which aims to improve the outflow of intraocular fluid and reduce intraocular pressure in glaucoma patients. They can also be used to create microtears on the cornea to facilitate fluid outflow and reduce pressure in the eye.
Vision Correction: Diode lasers are used in refractive vision correction surgery such as LASIK and PRK. They allow for precise and safe procedures to reshape the cornea of the eye to improve vision and eliminate the need for glasses or contact lenses.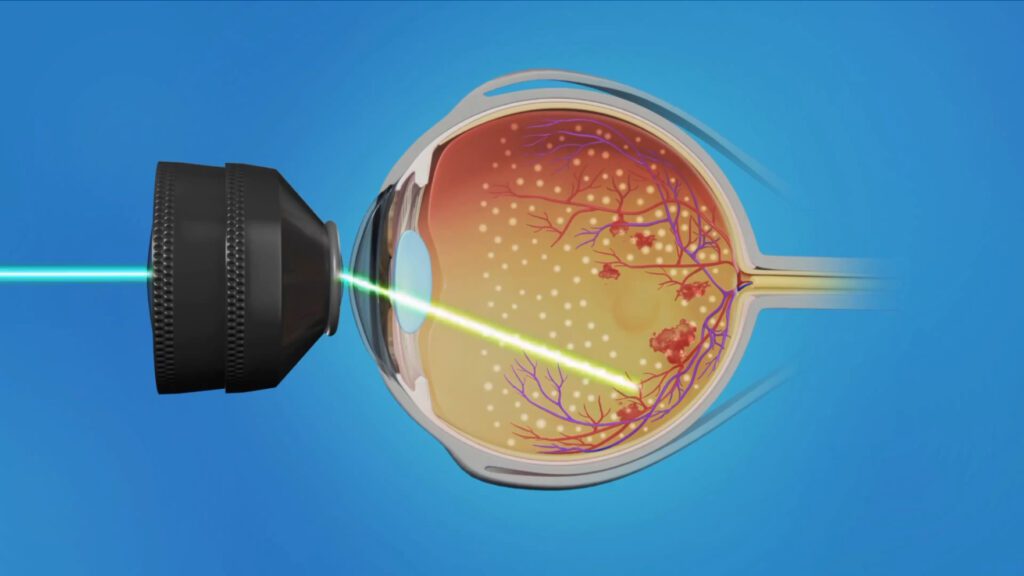
Retinal detachment treatment: Diode lasers can be used to perform laser photocoagulation procedures in cases of retinal detachment. Laser implants create a thermal effect on the retina which favors its attachment to the vasculature and prevents further detachment.
Advantages of diode lasers in ophthalmology:
High precision and controllability: Diode lasers allow ophthalmologists to achieve high precision and control during procedures. They can be fine-tuned to the right wavelength and intensity, allowing for precise treatment or surgery.
Minimal invasiveness: The use of diode lasers in ophthalmology allows for minimally invasive procedures. Due to the small size and high penetrating ability of the laser beam, most surgical interventions can be avoided, reducing the risk of complications and speeding up the recovery process.
Rapid healing: Laser procedures using diode lasers are usually accompanied by rapid healing. This is due to less damage to surrounding tissues, reduced risk of infection, and stimulation of regeneration.
Minimal discomfort for the patient: Procedures with diode lasers are usually not painful for patients. Local anesthesia or cooling systems may be used to ensure comfort during the procedure.